
Solar energy is the energy obtained by capturing heat and light from the Sun. Energy from the Sun is referred to as solar energy. Technology has provided a number of ways to utilize this abundant resource. It is considered a green technology because it does not emit greenhouse gases. Solar energy is abundantly available and has been utilized since long both as electricity and as a source of heat.
Solar power is the conversion of sunlight into electricity, either directly using photovoltaics (PV), or indirectly using concentrated solar power (CSP). CSP systems use lenses or mirrors and tracking systems to focus a large area of sunlight into a small beam. PV converts light into electric current using the photoelectric effect.
Solar power is anticipated to become the world’s largest source of electricity by 2050, with solar photovoltaics and concentrated solar power contributing 16 and 11 percent to the global overall consumption, respectively.[57] In 2016, after another year of rapid growth, solar generated 1.3% of global power.
How Solar Panels or PV Modules Work
In very basic terms, a solar panel (PV module) is a device that will produce a flow of electricity under sunlight. This electricity can be used to charge batteries and, with the aid of an inverter, it can power normal household electrical devices, or “loads”. PV modules can also be used in systems without batteries. Most solar panels (properly called “modules”) are framed in aluminum, topped with tempered glass, and sealed by a waterproof backing. Sandwiched between the glass and backing layers are the photo-reactive cells themselves, often made of silicon.
There are lots of ways to make use of solar electricity. One of the simplest is to charge small electronic devices, like cell phones and music players, with lightweight, portable PV modules. Solar panels can be used individually or wired together to form a solar array. For larger electrical loads, there are two main types of systems for providing electrical power to homes, cabins and offices, etc: stand-alone battery based systems (also called ‘off-grid’ systems) and grid-tied systems (also known as utility-interactive). You’ll want to decide which system is best for your needs by reading more about both.
Grid-Tied Solar Systems
Grid-tied, on-grid, utility-interactive, grid intertie and grid backfeeding are all terms used to describe the same concept – a solar system that is connected to the utility power grid.
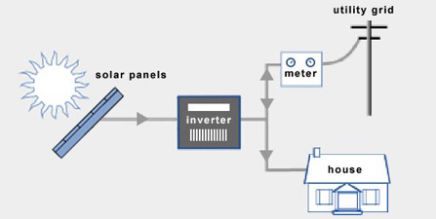
Advantages of Grid-Tied Systems
Save more money with Net Metering
A grid-connection will allow you to save more money with solar panels through better efficiency rates, net metering, plus lower equipment and installation costs
Grid-tied solar systems are therefore generally cheaper and simpler to install.
Your solar panels will often generate more electricity than what you are capable of consuming. With net metering, homeowners can put this excess electricity onto the utility grid instead of storing it themselves with batteries.
Net metering (or feed-in tariff schemes in some countries) play an important role in how solar power is incentivized. Without it, residential solar systems would be much less feasible from a financial point of view.
Electricity departments are committed to buying electricity from homeowners at the Rs. 3.20.
Grid-tie Inverter
What is the job of a solar inverter? They regulate the voltage and current received from your solar panels. Direct current (DC) from your solar panels is converted into alternating current (AC), which is the type of current that is utilized by the majority of electrical appliances.
Power Meter
Most homeowners will need to replace their current power meter with one that is compatible with net metering. This device, often called a net meter or a two-way meter, is capable of measuring power going in both directions, from the grid to your house and vice versa.
For more info Call us on +91 950 594 8888
Off-Grid Solar Systems
An off-grid solar system (off-the-grid, standalone) is the obvious alternative to one that is grid-tied. For homeowners that have access to the grid, off-grid solar systems are usually out of question. Here`s why.
To ensure access to electricity at all times, off-grid solar systems require battery storage and a backup generator (if you live off-the-grid). On top of this, a battery bank typically needs to be replaced after 10 years. Batteries are complicated, expensive and decrease overall system efficiency.
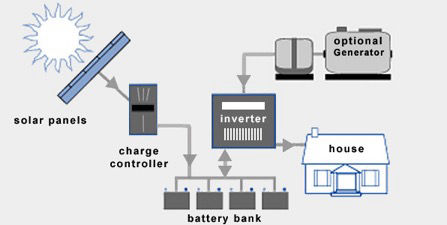
Advantages of Off-Grid Systems
Become energy self-sufficient
Living off the grid and being self-sufficient feels good. For some people, this feeling is worth more than saving money. Energy self-sufficiency is also a form of security. Power failures on the utility grid do not affect off-grid solar systems.
On the flip side, batteries can only store a certain amount of energy, and during cloudy times, being connected to the grid is actually where the security is. You should install a backup generator to be prepared for these kinds of situations.
No access to the utility grid
Off-grid solar systems can be cheaper than extending power lines in certain remote areas.
Only suitable in rural areas where electricity lines are hard to draw.
Extra components for Off-Grid Systems
Solar charge controller
Solar charge controllers are also known as charge regulators or just battery regulators. The last term is probably the best to describe what this device actually does: Solar battery chargers limit the rate of current being delivered to the battery bank and protect the batteries from overcharging.
Good charge controllers are crucial for keeping the batteries healthy, which ensures the lifetime of a battery bank is maximized. If you have a battery-based inverter, chances are that the charge controller is integrated.
Battery bank
Without a battery bank (or a generator) it’ll be lights out by sunset. A battery bank is essentially a group of batteries wired together.
DC Connect switch
AC and DC safety disconnects are required for all solar systems. For off-grid solar systems, one additional DC disconnect is installed between the battery bank and the off-grid inverter. It is used to switch off the current flowing between these components. This is important for maintenance, troubleshooting, and protection against electrical fires.
Off-Grid inverter
There’s no need for an inverter if you`re only setting up solar panels for your boat, your RV, or something else that runs on DC current. You will need an inverter to convert DC to AC for all other electrical appliances. Off-grid inverters do not have to match phase with the utility sine wave as opposed to grid-tie inverters. Electrical current flows from the solar panels through the solar charge controller and the bank battery bank before it is finally converted into AC by the off-grid-inverter.
Backup generator
It takes a lot of money and big batteries to prepare for several consecutive days without the sun shining (or access to the grid). This is where backup generators come in.
In most cases, installing a backup generator that runs on diesel is a better choice than investing in an oversized battery bank that seldom gets to operate at it`s full potential. Generators can run on propane, petroleum, gasoline and many other fuel types.
Backup generators typically output AC, which can be sent through the inverter for direct use, or it can be converted into DC for battery storage.
Hybrid Solar Systems
Hybrid solar systems combines the best from grid-tied and off-grid solar systems. These systems can either be described as off-grid solar with utility backup power, or grid-tied solar with extra battery storage.
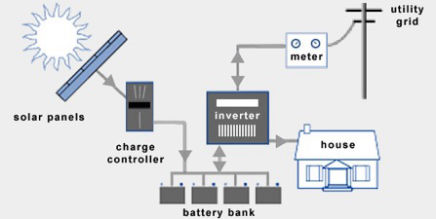
Advantages of Hybrid Solar Systems
Less expensive than Off-Grid System
Hybrid solar systems are less expensive than off-grid solar systems. You don’t really need a backup generator, and the capacity of your battery bank can be downsized. Off-peak electricity from the utility company is cheaper than diesel.
Smart solar holds a lot of promise
The introduction of hybrid solar systems has opened up for many interesting innovations. New inverters let homeowners take advantage of changes in the utility electricity rates throughout the day.
Solar panels happen to output the most electrical power at noon – not long before the price of electricity peaks. Consequently, you can temporarily store whatever excess electricity your solar panels in batteries, and put it on the utility grid when you are paid the most for every kWh.
Smart solar holds a lot of promise. The concept will become increasingly important as we transition towards the smart grid in the coming years.
Extra components for Hybrid Systems
Solar charge controller
Solar charge controllers are also known as charge regulators or just battery regulators. The last term is probably the best to describe what this device actually does: Solar battery chargers limit the rate of current being delivered to the battery bank and protect the batteries from overcharging.
Good charge controllers are crucial for keeping the batteries healthy, which ensures the lifetime of a battery bank is maximized. If you have a battery-based inverter, chances are that the charge controller is integrated.
Battery bank
Without a battery bank (or a generator) it’ll be lights out by sunset. A battery bank is essentially a group of batteries wired together.
DC Connect switch
AC and DC safety disconnects are required for all solar systems. For off-grid solar systems, one additional DC disconnect is installed between the battery bank and the off-grid inverter. It is used to switch off the current flowing between these components. This is important for maintenance, troubleshooting, and protection against electrical fires.
Battery based Grid-Tie Inverter
Hybrid solar systems utilize batter-based grid-tie inverters. These devices combine can draw electrical power to and from battery banks, as well as synchronize with the utility grid.
Power Meter
Most homeowners will need to replace their current power meter with one that is compatible with net metering. This device, often called a net meter or a two-way meter, is capable of measuring power going in both directions, from the grid to your house and vice versa.
For more info Call us on +91 950 594 8888
Advantages of Solar Energy
It increases access to energy
Though the deficiency of power in India is decreasing rapidly, still there are many people both in the rural and urban areas, who have improper and unreliable access to electricity. These people are forced to rely on alternatives like diesel generators. These alternatives pose harmful effects on the health and they are volatile in terms of their operating costs. In such a scenario, solar energy serves as an affordable source of electricity.
Support from the government
In order to encourage people to adopt solar energy, the government offers tax credits to those who install rooftop solar panels whether it be for residential or commercial purposes. As per the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy, the government pays 40% of the installation cost as a subsidy to the installer.
Reduces carbon footprints
Solar panels harness sunlight to generate electricity. So, they pose fewer pollution risks to the environment in comparison to conventional sources of energy. Unlike a generator, they run without producing any noise and give out lesser emissions of harmful gases. Furthermore, it is a good source of energy that combats climate change. Thus, rooftop solar is ideal as it reduces carbon footprints.
Green source of energy
This is an era where more and more people are adopting eco-friendly items. The consumers, especially industrial and commercial consumers, are willing to make capital investments to contribute towards the preservation of the environment. Environment-friendly customers are even willing to pay higher than grid power.
Low maintenance cost
The chief factor that accentuates the importance of rooftop solar panels is that they require very less maintenance. They come with a service life of over 20 years if maintained properly.
Suitable for Indian climate
Rooftop solar panels utilize sunlight to convert it into electricity. India is situated at an ideal geographical location and receives ample tropical sunlight. There are almost 300 sunny days with clear skies each year in India. Thus, rooftop solar panels are ideal to be used here.
Multiple applications of solar power
Along with the generation of electricity, solar power can meet several other purposes. It can be used to heat water and supply hot water or air to a building. It can also be used to run electric generators.
It doesn’t require additional space for installation
One of the biggest advantages of rooftop solar panels is that they can be installed on any type of roof. So, people don’t need to vacate a land or invest in buying additional land to set up rooftop solar panels. Furthermore, the panels offer protection to the roof of the building in which they are installed.

